Environments Design in InternNav#
This tutorial provided a step-by-step guide to define a new environment and a new navigation task within the InternNav framework.
Overview#
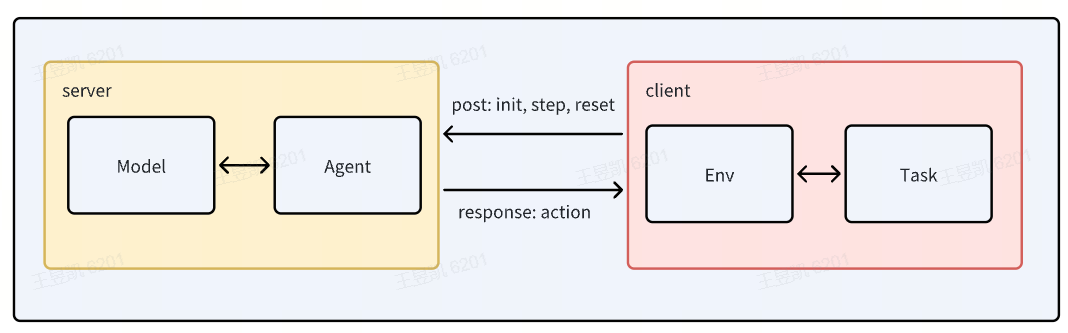
InternNav separates navigation logic / policy from where the agent actually lives (simulator vs real robot). The key ideas are:
Env: A unified interface. All environments must behave like anEnv.Task: A high-level navigation objective exposed to the agent, like “go to the kitchen sink” or “follow this instruction”.Agent: Agent consumes observations fromEnv, predicts an action, and sends that action back toEnv.
Because of this separation:
We can run the same agent in simulation (Isaac / InternUtopia) or on a real robot, as long as both environments implement the same API.
We can benchmark different tasks in different worlds without rewriting the agent.
InternNav already ships with three major environment backends:
InternUtopiaEnv: Simulated environment built on top of InternUtopia / Isaac Sim. This supports complex indoor scenes, object semantics, RGB-D sensing, and scripted evaluation loops.
HabitatEnv: Simulated environment built on top of Habitat Sim. This supports gym style workflow and handles distribution episodes set up.
RealWorldEnv: Wrapper around an actual robot platform and its sensors (e.g. RGB camera, depth, odometry). This lets you deploy the same agent logic in the physical world.
Both of these are children of the same base Env class.
Evaluation Metrics in VLN-PE#
For the VLN-PE benchmark in internutopia, InternNav provides comprehensive evaluation metrics:
Success Rate (SR): The proportion of episodes in which the agent successfully reaches the goal location within a 3-meter radius.
Success Rate weighted by Path Length (SPL): Measures both efficiency and success. It is defined as the ratio of the shortest-path distance to the actual trajectory length, weighted by whether the agent successfully reaches the goal. A higher SPL indicates that the agent not only succeeds but does so efficiently, without taking unnecessarily long routes.
Trajectory Length (TL): The total distance traveled by the agent during an episode, measured in meters.
Navigation Error (NE): The Euclidean distance (in meters) between the agent’s final position and the goal location at the end of an episode.
Oracle Success Rate (OSR): The proportion of episodes in which any point along the predicted trajectory comes within 3 meters of the goal—representing the agent’s potential success if it were to stop optimally.
Fall Rate (FR): The frequency at which the agent falls or loses balance during navigation.
Stuck Rate (StR): The frequency at which the agent becomes immobile or trapped (e.g., blocked by obstacles or unable to proceed).
Evaluation Metrics in VLN-CE#
For the VLN-CE benchmark in Habitat, InternNav keeps the original Habitat evaluation configuration and registers the following metrics:
Distance to Goal (DistanceToGoal): The geodesic distance from the agent’s current position to the goal location.
Success (Success): A binary indicator of whether the agent stops within 3 meters of the goal.
Success weighted by Path Length (SPL): Measures both success and navigation efficiency. It is defined as the ratio of the shortest-path distance to the actual trajectory length, weighted by whether the agent successfully reaches the goal. A higher SPL indicates that the agent not only succeeds but does so efficiently, without taking unnecessarily long routes.
Oracle Success Rate (OracleSuccess): The proportion of episodes in which any point along the agent’s trajectory comes within 3 meters of the goal, representing potential success if the agent were to stop optimally.
Oracle Navigation Error (OracleNavigationError): The minimum geodesic distance between the agent and the goal over the entire trajectory.
Normalized Dynamic Time Warping (nDTW): Measures how closely the agent’s trajectory follows the ground-truth demonstration path. Only registered in rxr benchmarks.
